Subtotal $0.00
Shopping cart
Subscribe to out newsletter today to receive latest news administrate cost effective for tactical data.
2478 Street City Ohio 90255
- Phone: 833-544-2779
Subscribe to out newsletter today to receive latest news administrate cost effective for tactical data.
2478 Street City Ohio 90255
Monday - Friday:9am - 6pm
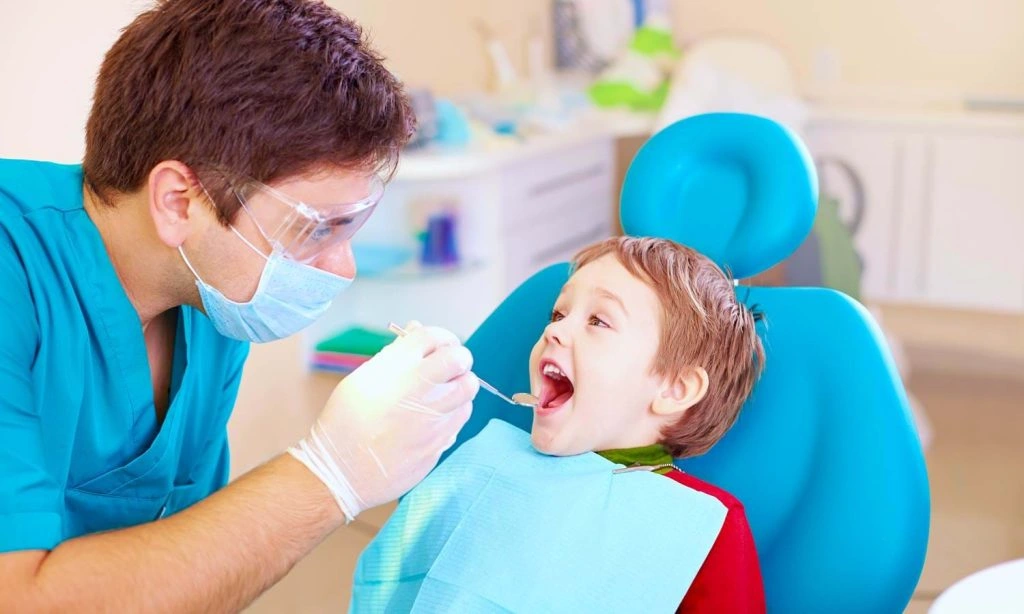
Pediatric dentistry primarily focuses on children from birth through adolescence. The American Dental Association (ADA) recognizes pediatric dentistry as a specialty, requiring dentists to undertake two or three years of additional training after completing a general dentistry degree. After this training, the American Board of Pediatric Dentistry issues a unique diploma (Diplomate ABPD).
One of the most important components of pediatric dentistry is child psychology. Pediatric dentists are trained to create a friendly, fun, social atmosphere for children and always avoid threatening words like “drill,” “needle,” and “injection.” Dental phobias beginning in childhood often continue into adulthood, so it is crucial that children have positive experiences and find their “dental home” as early as possible.
Pediatric dentists fulfill many important functions relating to a child’s oral health and hygiene, with a focus on the maintenance and care of deciduous (baby) teeth, which are crucial for good chewing habits, proper speech production, and holding space for permanent teeth.
Key functions include:
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry recommends that your child visit a pediatric dentist by their first birthday or within six months after the eruption of their first tooth. Early visits help establish a dental home and allow for guidance on proper oral care.
Regular checkups every six months are generally recommended. However, depending on your child's oral health, your pediatric dentist may suggest more frequent visits.
Primary (baby) teeth are crucial for proper chewing, speaking, and guiding permanent teeth into place. Neglecting their care can lead to pain, infection, and potential issues with developing permanent teeth.